Building Inclusive Communities: The Importance of Community Integration for Individuals with Disabilities
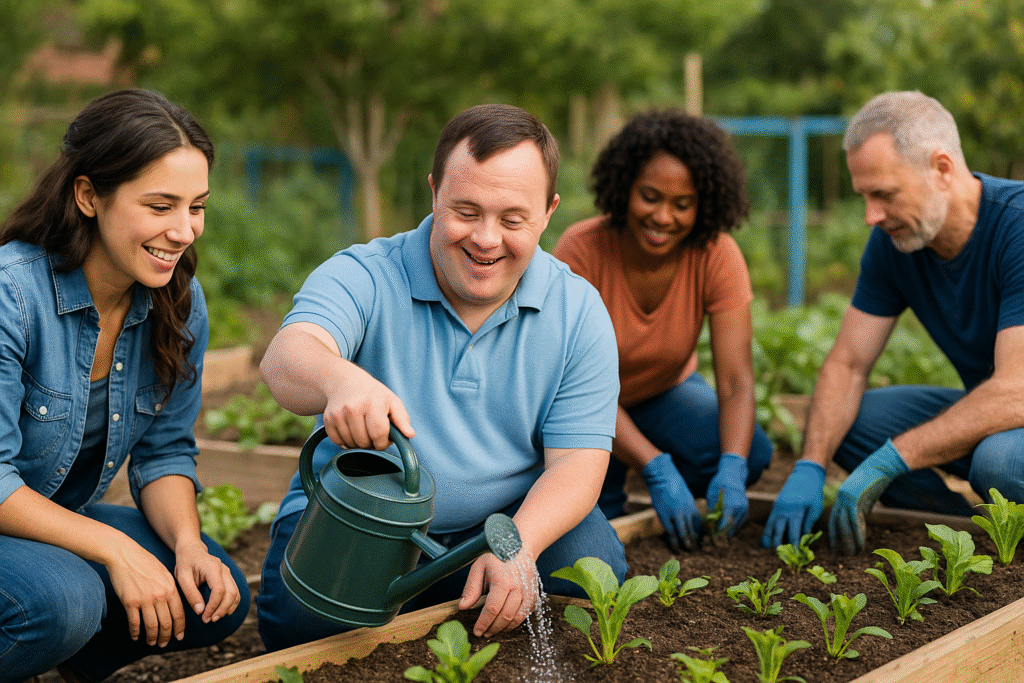
At Crescent Cila Homes, we believe that true quality of life extends beyond basic care—it encompasses meaningful participation in the broader community. This article explores the vital importance of community integration for individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities (IDDs) and how it creates stronger, more vibrant communities for everyone. Understanding Community Integration Community integration means that individuals with disabilities have the same opportunities as everyone else to: Live in typical housing within residential neighborhoods Work in competitive, integrated employment settings Build relationships with people with and without disabilities Access community resources and participate in community activities Contribute their unique gifts and talents to community life True integration goes beyond mere physical presence in the community—it involves genuine belonging, valued social roles, and meaningful participation. The Benefits of Community Integration Research consistently demonstrates that community integration leads to significant positive outcomes for individuals with disabilities: Enhanced quality of life and overall well-being Improved adaptive skills and greater independence Expanded social networks and natural supports Increased self-determination and personal choice Better health outcomes through active engagement Meaningful employment and economic self-sufficiency Reduced challenging behaviors through meaningful activities Benefits to the Broader Community Community integration doesn’t just benefit individuals with disabilities—it strengthens entire communities by: Promoting diversity and inclusion as community values Increasing awareness and understanding of disability issues Creating a more accessible environment that benefits everyone Developing innovative solutions to community challenges Enhancing local economies through workforce participation Building stronger social connections across diverse groups Enriching community life through unique contributions and perspectives Key Domains of Community Integration Comprehensive community integration addresses several important life domains: Residential Integration Scattered-site housing within typical neighborhoods Appropriate levels of support that promote maximum independence Homeownership or rental options like anyone else in the community Neighborhood involvement and relationship-building Access to transportation and community amenities Employment Integration Competitive employment at prevailing wages Integrated workplaces alongside people without disabilities Job customization that matches skills and interests Career advancement opportunities and ongoing development Entrepreneurship options for self-employment Social Integration Friendship development with people with and without disabilities Participation in community groups based on interests Relationship-building in natural community contexts Social skill development through authentic interactions Reciprocal relationships where people both give and receive support Recreational Integration Participation in community leisure activities and hobby groups Membership in fitness facilities and sports teams Attendance at cultural events and entertainment venues Outdoor recreation and nature activities Continuing education and lifelong learning opportunities Civic Integration Volunteering for community causes Voting and political participation Serving on boards and committees of community organizations Religious and spiritual participation in faith communities Advocacy for community improvements that benefit everyone Overcoming Barriers to Integration Despite its benefits, several barriers can impede successful community integration: Physical barriers – Inaccessible environments and transportation challenges Attitudinal barriers – Stigma, low expectations, and misconceptions Policy barriers – Funding structures that favor segregated settings Knowledge barriers – Lack of information about effective inclusion strategies Support barriers – Insufficient or inflexible support systems Addressing these barriers requires a coordinated approach involving multiple stakeholders, including individuals with disabilities, families, service providers, policymakers, and community members. Strategies for Promoting Community Integration Effective community integration employs multiple strategies: Individual-Level Strategies Person-centered planning that identifies integration goals and needed supports Skill development in areas that facilitate community participation Self-advocacy training to help individuals express their preferences Natural support development to reduce reliance on paid supports Technology utilization to enhance independence and communication Family-Level Strategies Education about integration benefits and available resources Connection with other families who have achieved successful integration Vision-building for community-based futures Navigation assistance through complex support systems Respite services to support ongoing family involvement Provider-Level Strategies Staff training in community inclusion practices Flexible support models that adapt to community settings Community resource mapping to identify opportunities Partnership development with community organizations Transportation solutions that enable community access Community-Level Strategies Disability awareness initiatives that highlight capabilities Universal design approaches to make environments accessible to all Business engagement to promote inclusive hiring practices Community organization capacity-building for inclusive programming Policy advocacy for systems change that supports integration The Role of Community Resource Mapping Community resource mapping is a powerful tool for identifying integration opportunities: Identify community assets – Businesses, organizations, groups, and facilities Determine accessibility status – Physical access, sensory accommodations, etc. Explore potential partnerships – Find allies for inclusion efforts Match resources to interests – Connect individuals to opportunities based on preferences Develop access strategies – Create plans to overcome any barriers Success Stories: Community Integration in Action Community integration can take many forms, as illustrated by these success stories: John, who has Down syndrome, works at a local bakery three days a week, has his own apartment with drop-in support, and plays in a community softball league Maria, who has autism, volunteers at an animal shelter, participates in a book club at the library, and shares an apartment with a roommate David, who has cerebral palsy, runs an online business from his home, serves on a neighborhood association board, and mentors young people with disabilities These examples demonstrate that with the right supports and opportunities, meaningful community integration is achievable for individuals with a wide range of abilities. How Crescent Cila Homes Supports Community Integration At Crescent Cila Homes, our approach to community integration includes: Community-based housing with appropriate, flexible supports Individualized community participation plans based on personal interests Transportation assistance to access community activities Community connector staff who facilitate relationship development Partnership with local employers to create job opportunities Collaboration with community organizations to enhance inclusion Ongoing evaluation of integration outcomes and quality of life Getting Started with Community Integration For families and individuals interested in enhancing community integration: Start with the person’s interests and strengths Begin with one or two integration goals Identify potential community settings that match interests Consider what supports might be needed Take small steps and build on successes Connect with others who have achieved successful integration Advocate for needed policy and system changes To learn more about our community integration approach at Crescent Cila Homes, contact us